Indian Railways began its journey in 1853 with a steam-powered train running from Mumbai to Thane. Over time, steam engines became iconic, filling platforms with their chugging sounds and billowing smoke. The steam locomotive, once a symbol of Indian transportation, remains a nostalgic memory for many.
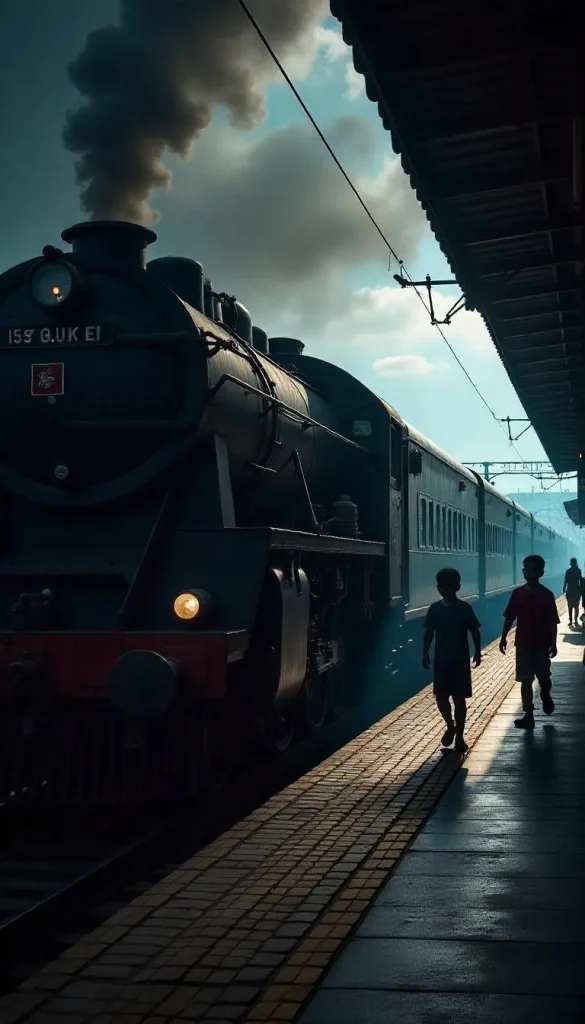
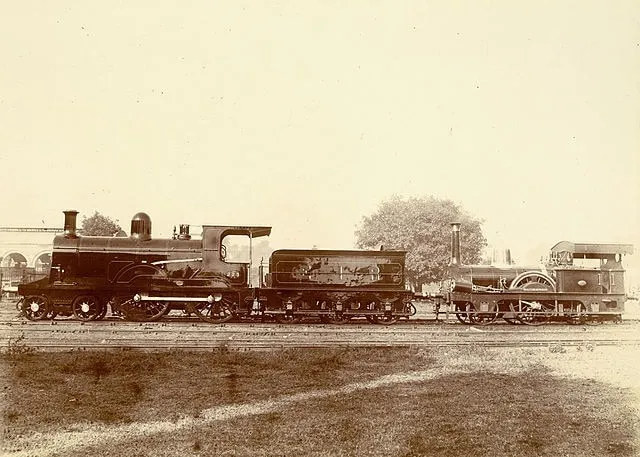
The First Indian Steam Locomotive
India produced its first steam engine in 1895 at the Ajmer workshop. This was a pivotal moment, marking India’s entry into locomotive manufacturing. The engine served the railways for over six decades before being retired in 1958.
Evolution of Indian Railways
The first railway line was proposed in Madras in 1832, leading to the creation of India’s first railway track by 1837. The late 19th century saw the formation of major railways like the Madras Railway and the Great Indian Peninsular Railway. By the early 20th century, the introduction of electrified trains marked a new era in railway development.
Electrification and Expansion
In 1925, India’s first Railway Budget was introduced alongside the electrification of the railways. This period also saw the unification of the railway system in 1944, consolidating 42 railway companies into the national network.

Post-Independence Milestones
The creation of the Chittaranjan Locomotive Works in 1950 helped India develop its first indigenous steam engine. By 1951, Indian Railways began its reorganisation into regional zones, improving efficiency. This era also saw the introduction of faster trains like the Shatabdi Express and computerised ticketing.
The Vande Bharat Revolution
The launch of the Vande Bharat Express in 2019 marked a significant leap for Indian Railways. This semi-high-speed train, built entirely in India, symbolised the country’s progress toward faster, more efficient rail travel. The upcoming Mumbai-Ahmedabad Bullet Train, set for completion by 2026, will further enhance speed and connectivity.

A Look Ahead: High-Speed Rail Network
The Bullet Train project, a collaboration with Japan, promises to revolutionise travel between Mumbai and Ahmedabad, reducing travel time dramatically and setting a new standard for high-speed rail in India.
From its humble beginnings with steam locomotives to the cutting-edge Vande Bharat Express and Bullet Train projects, Indian Railways continues to evolve. This journey not only connects millions of people but also reflects India’s resilience and ambition to build a modern, efficient, and interconnected rail network.
