The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has revealed details about its ambitious Aditya-L1 Mission, which aims to study the dynamics of the Sun and space weather. Here are the key points about the mission:
Aditya-L1 Mission
Aditya-L1 is India’s first space-based observatory designed to study the Sun’s behavior and space weather phenomena.
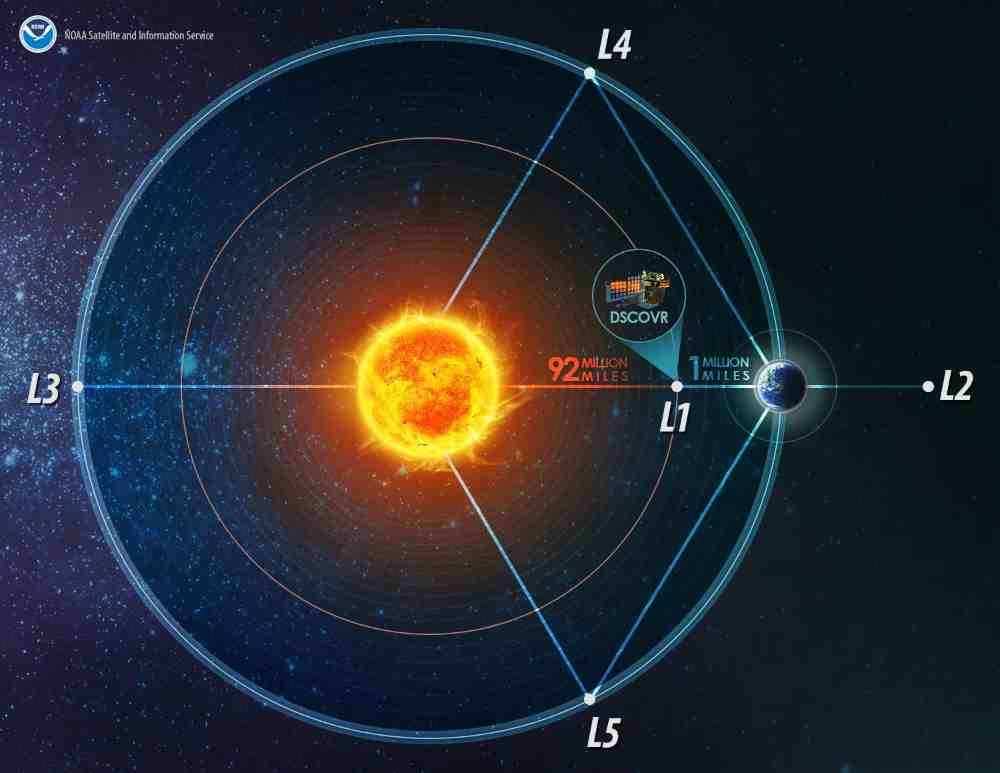
The spacecraft will be placed in a halo orbit around the Lagrange Point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, which is located about 1.5 million kilometers from Earth.

Payloads
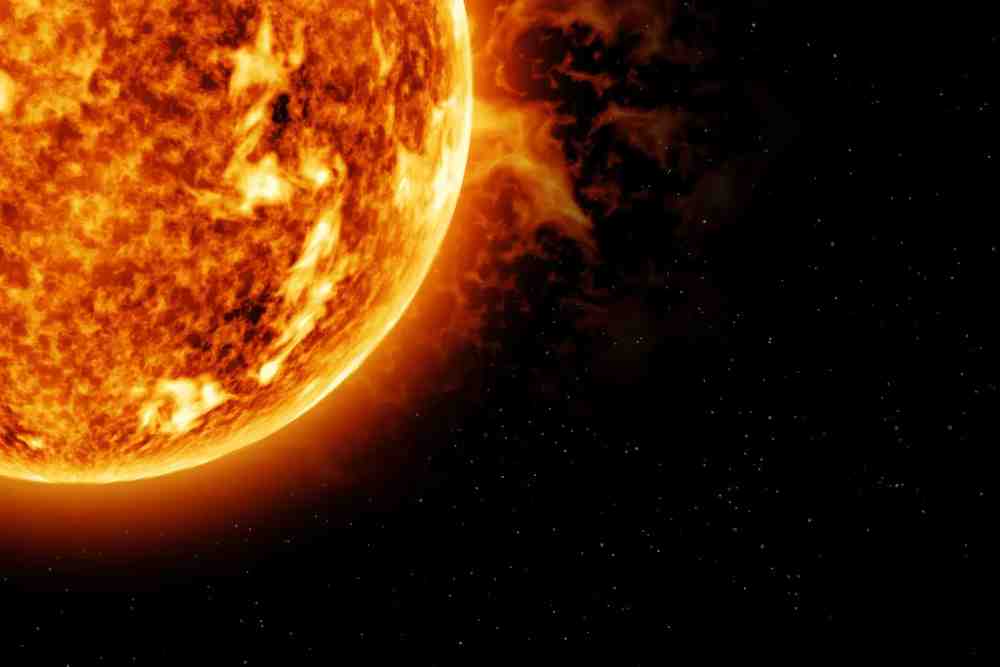
The satellite carries seven scientific payloads that are equipped to observe different layers of the Sun, including the photosphere, chromosphere, and the outermost layer (corona).
These payloads consist of electromagnetic and particle detectors, as well as magnetic field detectors.
Mission Goals
Aditya-L1 aims to provide valuable insights into various solar phenomena such as coronal heating, coronal mass ejections, pre-flare and flare activities, space weather dynamics, and the propagation of particles and fields.
The mission is expected to contribute to a better understanding of the physics of the solar corona, its heating mechanism, magnetic field topology, and the development of coronal mass ejections.

Real-time Observation
The satellite’s location in orbit will allow it to continuously observe the Sun without interruptions from eclipses or occultation events. This will enable scientists to monitor solar activities and their effects on space weather in real-time.
Significance
Aditya-L1 is expected to provide groundbreaking insights into the behavior of the Sun and its impact on space weather, which has implications for technologies like satellites, communication systems, and power grids on Earth.
This mission is a significant step towards advancing India’s capabilities in space research and understanding fundamental solar processes.
Development and Launch
The satellite for the Aditya-L1 Mission was developed at the U R Rao Satellite Centre (URSC) in Bengaluru, India.
While the exact launch date is yet to be announced, the satellite has arrived at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC-SHAR) in Sriharikota, India, in preparation for its launch.

International Collaboration
The mission aligns with global efforts to study and understand the Sun’s behavior and space weather phenomena.
Aditya-L1’s scientific data and observations are expected to contribute to the broader scientific community’s knowledge of solar dynamics and their effects.
Overall, the Aditya-L1 Mission represents a significant advancement in India’s space exploration efforts, providing new insights into solar processes and enhancing our understanding of space weather.
